In studying “Investment Decisions” for the CMA, you should learn to evaluate various types of investments by analyzing cash flows, risks, and returns to make sound financial decisions. Understand capital budgeting techniques, including net present value (NPV), internal rate of return tax deductions guide, 20 popular breaks in 2021 (IRR), and payback period, and how to apply them to assess project viability. Analyze the impact of investment decisions on a company’s financial health and strategic goals. Evaluate the role of cost of capital in decision-making and explore the trade-offs between risk and return.
Why is Net Present Value (NPV) Analysis Used?
Net Present Value (NPV) is a financial metric that assesses the profitability of an investment by comparing the present value of expected future cash flows to the initial investment. It considers the time value of money, recognizing that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. If the difference is positive, it’s a profitable project and if it is negative, then it’s not worthy.
Alternative Investment Evaluation Methods
NVP is also an important indicator of how profitable a potential investment in another business will be and is often used as part of investors’ overall appraisal. If you went to college or university, you probably learned what NPV and IRR were and you may have even memorized the formula. If it’s been awhile since you have last thought through these calculations we are here to help dust off the cobwebs and give you a bit of a refresher.
- Performing NPV analysis is a practical method to determine the economic feasibility of undertaking a potential project or investment.
- The project will require purchase of fixed assets of $550,000 which is to be depreciated using straight-line method with a salvage value of $150,000.
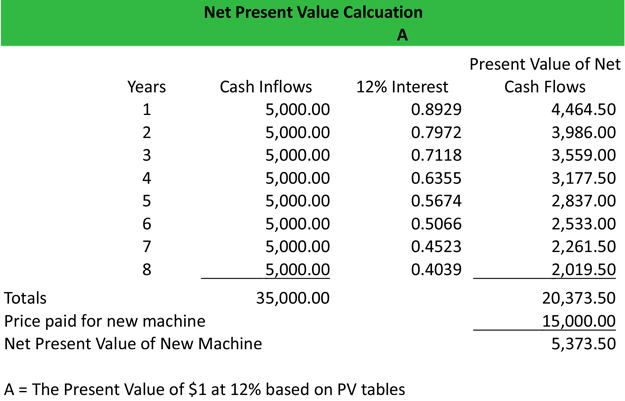
- Net present value is a financial calculation used to determine the present value of future cash flows.
- Therefore, XNPV is a more practical measure of NPV, considering cash flows are usually generated at irregular intervals.
Get up to $1,000 in stock when you fund a new Active Invest account.*
Each of the cash flows in the forecast and terminal value is then discounted back to the present using a hurdle rate of the firm’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). Calculating the payback period helps determine how long to hold onto an investment. You might use this method if you’re trying to compare multiple investments to see which one is a better fit for your personal investing timeline. But if you want to get a sense of the total return you’re likely to realize, then you’d still want to apply the net present value formula. The payback period is the period of time required for a return on investment to equal the initial investment.
NPV vs IRR Video
But this is still considered a positive NPV, and indicates that the investment opportunity is worthwhile. But you know that this future money is worth less than today’s money, so you want to get a more accurate picture by using the Net Present Value Calculation. ‘Time value of money’ is the concept that money you have now, in the present, is worth more than any future money.
This is the foundation of working out the overall Net Present Value of a project or investment. Net Present Value is an accounting calculation that’s used to help make decisions about investments. It’s more useful than some other investment indicators because it takes the ‘time value of money’ into account. Our manual calculation of net present value and Excel NPV assumes that cash flows occur at the period-end. If we want to determine net present value based on the exact date those cash flows occur, we can use Excel XNPV function.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
The cost of capital is the rate of return that an organization must earn on its investments to satisfy investors and lenders. It serves as a benchmark for evaluating new projects and investments, guiding financial decisions to ensure that returns meet or exceed investor expectations. Understanding the role of cost of capital is critical for making informed strategic and financial decisions. Net present value, on the other hand, is the sum of the present values for both cash inflows and cash outflows. With the NPV formula, you’re trying to determine how profitable an investment might be, based on the initial investment required and expected rate of return.
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets, managed by professionals. In case of standalone projects, accept a project only if its NPV is positive, reject it if its NPV is negative and stay indifferent between accepting or rejecting if NPV is zero. This means that this is a bad investment, on track to make a loss and not worth the risk.
The payback period is the time required for an investment or project to recoup its initial costs. Shorter payback periods are generally more attractive, as they indicate faster recovery of the initial investment. NPV takes into account both the magnitude and timing of cash flows, providing a more accurate representation of an investment or project’s profitability compared to other methods that may not consider these factors. A positive NPV indicates that the projected earnings from an investment exceed the anticipated costs, representing a profitable venture.
If the NPV is negative, it indicates that the investment is not expected to generate enough cash flows to cover the initial investment and is therefore a bad investment. The NPV formula is a way of calculating the Net Present Value (NPV) of a series of cash flows based on a specified discount rate. The NPV formula can be very useful for financial analysis and financial modeling when determining the value of an investment (a company, a project, a cost-saving initiative, etc.).

Leave A Comment